Protein prime quality has obtained a great deal of consideration in present issues with MASS Evaluation Overview, and for good objective – loads of utilized analysis have challenged some mechanistically pushed assumptions about how a protein provide’s amino acid profile and normal prime quality ranking might affect its functionality to help hypertrophy. This dialog normally entails evaluating a lower-quality plant-based protein to a higher-quality animal-based protein, and updated analysis have steered that plant-based proteins can efficiently help hypertrophy when complete protein consumption is ≥1.6g/kg/day (2). This isn’t on account of 1.6 is a magic amount and ensures optimum useful properties. Comparatively, we see that lower-quality proteins are sometimes significantly “inefficient” protein sources nonetheless normally have complementary amino acid safety, so their suitability (by the use of maximally supporting hypertrophy) depends upon complete protein consumption. When complete protein consumption is extreme, the effectivity of each explicit particular person protein provide turns into a lot much less associated, nonetheless when complete protein consumption will get lower and reduce, effectivity turns into increasingly very important.
It’s very important to acknowledge, however, that the protein prime quality dialog isn’t on a regular basis about evaluating plant sources to animal sources. Collagen is a fairly widespread animal-based protein, nonetheless it has a very low protein prime quality ranking (zero, in precise reality). Collagen has a very atypical amino acid profile; it lacks tryptophan utterly (subsequently the protein prime quality ranking of zero) and a variety of different completely different necessary amino acids, nonetheless has very extreme portions of glycine, proline, hydroxyproline, and hydroxylysine. Its amino acid profile could also be very conducive to collagen synthesis, which could theoretically be good for bones, tendons, and completely different connective tissues. In distinction, its amino acid profile is pretty horrible for supporting hypertrophy, with comparatively low portions of significant necessary amino acids just like leucine, isoleucine, valine, lysine, methionine, and threonine.
The amino acid shortcomings of collagen are pretty a bit completely completely different than the amino acid state of affairs for a lot of plant-based proteins. When you occur to try this open-access overview by Van Vliet and colleagues (3), you presumably can study amino acid parts of assorted plant-based and animal-based proteins. You’ll uncover that plant-based selections are sometimes just a little bit lower in leucine (nonetheless not outrageously so), and may are more likely to lack one or two necessary amino acids, with a relative abundance of others. As an example, you presumably can match a protein like lentils (low methionine, extreme lysine) with a protein like rice (extreme methionine, low lysine), and end up with a reasonably full normal amino acid profile. In distinction, the widespread amino acid shortcomings of collagen would possibly most likely be just a little bit more durable to rectify. No matter these fairly a couple of amino acid shortfalls, the evaluation assessing collagen’s affect on longitudinal modifications in fat-free mass is mixed, with a shocking number of analysis reporting will improve (4).
To extra uncover collagen’s potential for supporting hypertrophy and useful properties in fat-free mass, the presently reviewed study (1) in distinction post-workout supplementation with 35 grams of whey protein to 35 grams of leucine-enriched collagen over the course of a 10-week resistance teaching program. Every dietary dietary supplements contained 35 grams of complete protein and three grams of leucine, which required that a further 2 grams of leucine be added to the collagen complement. The protein dietary dietary supplements supplied about 0.5g/kg/day of protein, which was consumed on excessive of people’ abnormal protein consumption (which was spherical 1.1-1.5 g/kg/day, on widespread). Supervised teaching durations occurred three days per week, and dietary dietary supplements have been consumed throughout the night time on non-training days. This technique consisted of full-body workouts with a variety of models per practice and repetitions throughout the 8-12 per set differ, and lots more and plenty have been adjusted weekly to ensure that this technique was progressive in nature. 18 healthful youthful adults (aged 18 to 35) have been randomly assigned to each group, nonetheless solely 11 people (8 males and three women) from each group have been able to finish the entire study with acceptable adherence.
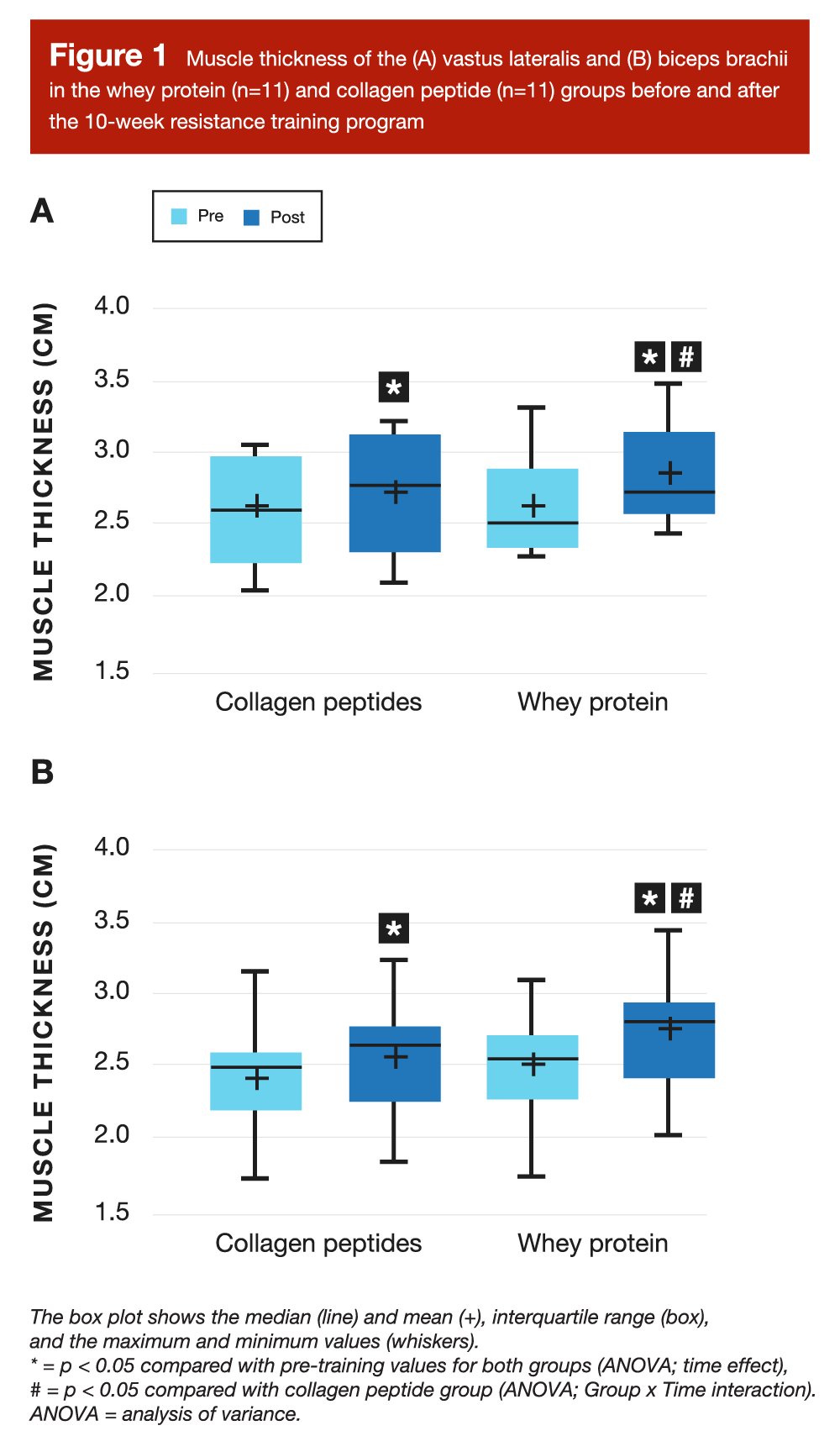
By the use of study outcomes, the researchers have been primarily excited by assessing modifications in teaching load, isokinetic elbow flexor power and power, lower-body peak power (measured by the use of countermovement bounce), and muscle thickness of the vastus lateralis and biceps brachii (measured by the use of ultrasound). There have been no statistically very important variations between groups by the use of teaching load, lower-body peak power, or isokinetic elbow flexor power or power. Nonetheless, the whey group expert significantly greater will improve in vastus lateralis and biceps brachii muscle thickness than the collagen group (Decide 1). The whey group expert Cohen’s d influence sizes of 0.68 and 0.61 for will improve in vastus lateralis and biceps brachii thickness, whereas the collagen group expert influence sizes of solely 0.38 and 0.35, respectively.

Whole, these outcomes aren’t utterly beautiful. As talked about by the authors of the present study (1), there are some analysis reporting will improve in fat-free mass following collagen supplementation, nonetheless the one study that immediately measured muscle hypertrophy found no very important influence of collagen supplementation on muscle progress. Furthermore, although we shouldn’t assume that acute muscle protein synthesis fees are utterly indicative of hypertrophic potential, there’s direct evaluation exhibiting that that collagen has underwhelming outcomes on acute muscle protein synthesis (5), thereby linking the acute, mechanistic findings to the longitudinal, utilized findings.
An attention-grabbing assertion throughout the presently reviewed study is that non-supplement protein consumption fell over time throughout the collagen group, and was a bit lower than the whey group. Meals routine logs have been analyzed at baseline, along with weeks 3, 7, and 10. The collagen group started spherical 1.5g/kg/day, and steadily dropped to 1.2g/kg/day in week 7, and finally to 1.1g/kg/day in week 10. In distinction, the whey group consumed 1.4g/kg/day the least bit time components apart from week 3 (1.1g/kg/day). A reasonably fixed discovering throughout the literature evaluating plant and animal proteins is that plant-based proteins are more likely to do improbable, as long as complete protein consumption is ≥1.6g/kg/day. Throughout the present study, the leucine-enriched collagen should have pushed the collagen group to or above that threshold (1.1-1.5 g/kg/day of protein from meals, plus 0.5g/kg/day of protein from the collagen complement). So, it can appear that this primary rule tends to hold true for diets composed of typical plant proteins (that are more likely to have reasonably passable and complementary amino acid profiles), nonetheless collagen’s amino acid profile is just too flawed for this guideline to make use of (even after leucine fortification). As soon as extra, this shouldn’t be a whole shock, offered that collagen’s amino acid points lengthen far previous leucine alone.
So, in case you’re focused on hypertrophy and fascinated with altering some moderate- or high-quality dietary proteins with collagen dietary dietary supplements, you’ll want to rethink that method. I normally don’t advocate for convoluted protein-counting strategies (for example, counting solely high-quality protein sources in direction of your daily protein complete, or counting low- or moderate-quality proteins in a fractional methodology), and I obtained’t start now. Nonetheless, I’d advise hypertrophy-focused readers in opposition to consuming a considerable portion of daily protein from collagen, and if an enormous dose of collagen (for example, >15g/day) is part of your daily routine, it’s possible you’ll want to double check to ensure that your complete daily protein consumption is as a minimum throughout the differ of 1.7-1.8 g/kg/day. I’ve beforehand described some plant-based proteins as being “inefficient” for promoting hypertrophy (when scaled relative to caloric content material materials or complete protein content material materials), nonetheless this turns into a lot much less very important when complete protein consumption meets or exceeds 1.6g/kg/day. Collagen happens to be very, very inefficient, so that you simply’ll most likely want to be at or above the 1.7-1.8 g/kg/day differ to ensure that this inefficiency isn’t hindering muscle progress. To be clear, that fluctuate simply isn’t empirically derived, and is a bit speculative. You would possibly argue regarding the exact complete protein amount that have to be reached, nonetheless the fundamental degree is that you just don’t want to be altering a great deal of high-quality or moderate-quality proteins with collagen in case you’re near the lower end of the optimum protein differ.
You is probably questioning why people would hassle with collagen supplementation throughout the first place. As I reviewed in a earlier MASS article, there’s some proof to suggest that collagen supplementation can facilitate collagen synthesis and is also useful for individuals with joint ache or completely different factors related to connective tissues. This physique of study is small, and it’s not universally embraced by sports activities actions weight loss plan consultants, nonetheless there’s as a minimum some proof linking collagen supplementation to elevated fees of collagen synthesis, elevated fat-free mass (presumably by the use of elevated connective tissue mass), and attenuation of joint ache.
I’m not a connective tissue expert, so take this with a grain of salt, nonetheless I’m personally not sure that collagen supplementation will be my first plan of motion if I was dealing with a connective tissue hurt that wished some dietary help. I really feel it’s possible you’ll make a robust argument that the glycine content material materials is nearly undoubtedly driving the results of collagen supplementation (6), and as a fringe revenue, there’s moreover proof linking glycine to raised sleep (7). Kidney stones don’t seem like a notable drawback throughout the longitudinal analysis on collagen supplementation, nonetheless it’s worth noting that collagen is rich in hydroxyproline, which could theoretically improve the prospect of kidney stones (8). As such, aiming for 3-5g of glycine is probably an acceptable completely different to taking 10-15g of collagen. So, in summary, there’s some proof linking collagen supplementation to modest benefits related to connective tissues and joints, nonetheless it’s pretty doable that just a little bit little little bit of glycine would do the trick. Each method, you don’t want to rely carefully on collagen for the promotion of muscle hypertrophy, and in case you happen to devour a substantial amount of collagen, you’ll want to make sure you’re taking obligatory steps to realize passable and full necessary amino acid consumption.
Related
Protein prime quality has obtained a great deal of consideration in present issues with MASS Evaluation Overview, and for good objective – loads of utilized analysis have challenged some mechanistically pushed assumptions about how a protein provide’s amino acid profile and normal prime quality ranking might affect its functionality to help hypertrophy. This dialog normally entails evaluating a lower-quality plant-based protein to a higher-quality animal-based protein, and updated analysis have steered that plant-based proteins can efficiently help hypertrophy when complete protein consumption is ≥1.6g/kg/day (2). This isn’t on account of 1.6 is a magic amount and ensures optimum useful properties. Comparatively, we see that lower-quality proteins are sometimes significantly “inefficient” protein sources nonetheless normally have complementary amino acid safety, so their suitability (by the use of maximally supporting hypertrophy) depends upon complete protein consumption. When complete protein consumption is extreme, the effectivity of each explicit particular person protein provide turns into a lot much less associated, nonetheless when complete protein consumption will get lower and reduce, effectivity turns into increasingly very important.
It’s very important to acknowledge, however, that the protein prime quality dialog isn’t on a regular basis about evaluating plant sources to animal sources. Collagen is a fairly widespread animal-based protein, nonetheless it has a very low protein prime quality ranking (zero, in precise reality). Collagen has a very atypical amino acid profile; it lacks tryptophan utterly (subsequently the protein prime quality ranking of zero) and a variety of different completely different necessary amino acids, nonetheless has very extreme portions of glycine, proline, hydroxyproline, and hydroxylysine. Its amino acid profile could also be very conducive to collagen synthesis, which could theoretically be good for bones, tendons, and completely different connective tissues. In distinction, its amino acid profile is pretty horrible for supporting hypertrophy, with comparatively low portions of significant necessary amino acids just like leucine, isoleucine, valine, lysine, methionine, and threonine.
The amino acid shortcomings of collagen are pretty a bit completely completely different than the amino acid state of affairs for a lot of plant-based proteins. When you occur to try this open-access overview by Van Vliet and colleagues (3), you presumably can study amino acid parts of assorted plant-based and animal-based proteins. You’ll uncover that plant-based selections are sometimes just a little bit lower in leucine (nonetheless not outrageously so), and may are more likely to lack one or two necessary amino acids, with a relative abundance of others. As an example, you presumably can match a protein like lentils (low methionine, extreme lysine) with a protein like rice (extreme methionine, low lysine), and end up with a reasonably full normal amino acid profile. In distinction, the widespread amino acid shortcomings of collagen would possibly most likely be just a little bit more durable to rectify. No matter these fairly a couple of amino acid shortfalls, the evaluation assessing collagen’s affect on longitudinal modifications in fat-free mass is mixed, with a shocking number of analysis reporting will improve (4).
To extra uncover collagen’s potential for supporting hypertrophy and useful properties in fat-free mass, the presently reviewed study (1) in distinction post-workout supplementation with 35 grams of whey protein to 35 grams of leucine-enriched collagen over the course of a 10-week resistance teaching program. Every dietary dietary supplements contained 35 grams of complete protein and three grams of leucine, which required that a further 2 grams of leucine be added to the collagen complement. The protein dietary dietary supplements supplied about 0.5g/kg/day of protein, which was consumed on excessive of people’ abnormal protein consumption (which was spherical 1.1-1.5 g/kg/day, on widespread). Supervised teaching durations occurred three days per week, and dietary dietary supplements have been consumed throughout the night time on non-training days. This technique consisted of full-body workouts with a variety of models per practice and repetitions throughout the 8-12 per set differ, and lots more and plenty have been adjusted weekly to ensure that this technique was progressive in nature. 18 healthful youthful adults (aged 18 to 35) have been randomly assigned to each group, nonetheless solely 11 people (8 males and three women) from each group have been able to finish the entire study with acceptable adherence.
By the use of study outcomes, the researchers have been primarily excited by assessing modifications in teaching load, isokinetic elbow flexor power and power, lower-body peak power (measured by the use of countermovement bounce), and muscle thickness of the vastus lateralis and biceps brachii (measured by the use of ultrasound). There have been no statistically very important variations between groups by the use of teaching load, lower-body peak power, or isokinetic elbow flexor power or power. Nonetheless, the whey group expert significantly greater will improve in vastus lateralis and biceps brachii muscle thickness than the collagen group (Decide 1). The whey group expert Cohen’s d influence sizes of 0.68 and 0.61 for will improve in vastus lateralis and biceps brachii thickness, whereas the collagen group expert influence sizes of solely 0.38 and 0.35, respectively.

Whole, these outcomes aren’t utterly beautiful. As talked about by the authors of the present study (1), there are some analysis reporting will improve in fat-free mass following collagen supplementation, nonetheless the one study that immediately measured muscle hypertrophy found no very important influence of collagen supplementation on muscle progress. Furthermore, although we shouldn’t assume that acute muscle protein synthesis fees are utterly indicative of hypertrophic potential, there’s direct evaluation exhibiting that that collagen has underwhelming outcomes on acute muscle protein synthesis (5), thereby linking the acute, mechanistic findings to the longitudinal, utilized findings.
An attention-grabbing assertion throughout the presently reviewed study is that non-supplement protein consumption fell over time throughout the collagen group, and was a bit lower than the whey group. Meals routine logs have been analyzed at baseline, along with weeks 3, 7, and 10. The collagen group started spherical 1.5g/kg/day, and steadily dropped to 1.2g/kg/day in week 7, and finally to 1.1g/kg/day in week 10. In distinction, the whey group consumed 1.4g/kg/day the least bit time components apart from week 3 (1.1g/kg/day). A reasonably fixed discovering throughout the literature evaluating plant and animal proteins is that plant-based proteins are more likely to do improbable, as long as complete protein consumption is ≥1.6g/kg/day. Throughout the present study, the leucine-enriched collagen should have pushed the collagen group to or above that threshold (1.1-1.5 g/kg/day of protein from meals, plus 0.5g/kg/day of protein from the collagen complement). So, it can appear that this primary rule tends to hold true for diets composed of typical plant proteins (that are more likely to have reasonably passable and complementary amino acid profiles), nonetheless collagen’s amino acid profile is just too flawed for this guideline to make use of (even after leucine fortification). As soon as extra, this shouldn’t be a whole shock, offered that collagen’s amino acid points lengthen far previous leucine alone.
So, in case you’re focused on hypertrophy and fascinated with altering some moderate- or high-quality dietary proteins with collagen dietary dietary supplements, you’ll want to rethink that method. I normally don’t advocate for convoluted protein-counting strategies (for example, counting solely high-quality protein sources in direction of your daily protein complete, or counting low- or moderate-quality proteins in a fractional methodology), and I obtained’t start now. Nonetheless, I’d advise hypertrophy-focused readers in opposition to consuming a considerable portion of daily protein from collagen, and if an enormous dose of collagen (for example, >15g/day) is part of your daily routine, it’s possible you’ll want to double check to ensure that your complete daily protein consumption is as a minimum throughout the differ of 1.7-1.8 g/kg/day. I’ve beforehand described some plant-based proteins as being “inefficient” for promoting hypertrophy (when scaled relative to caloric content material materials or complete protein content material materials), nonetheless this turns into a lot much less very important when complete protein consumption meets or exceeds 1.6g/kg/day. Collagen happens to be very, very inefficient, so that you simply’ll most likely want to be at or above the 1.7-1.8 g/kg/day differ to ensure that this inefficiency isn’t hindering muscle progress. To be clear, that fluctuate simply isn’t empirically derived, and is a bit speculative. You would possibly argue regarding the exact complete protein amount that have to be reached, nonetheless the fundamental degree is that you just don’t want to be altering a great deal of high-quality or moderate-quality proteins with collagen in case you’re near the lower end of the optimum protein differ.
You is probably questioning why people would hassle with collagen supplementation throughout the first place. As I reviewed in a earlier MASS article, there’s some proof to suggest that collagen supplementation can facilitate collagen synthesis and is also useful for individuals with joint ache or completely different factors related to connective tissues. This physique of study is small, and it’s not universally embraced by sports activities actions weight loss plan consultants, nonetheless there’s as a minimum some proof linking collagen supplementation to elevated fees of collagen synthesis, elevated fat-free mass (presumably by the use of elevated connective tissue mass), and attenuation of joint ache.
I’m not a connective tissue expert, so take this with a grain of salt, nonetheless I’m personally not sure that collagen supplementation will be my first plan of motion if I was dealing with a connective tissue hurt that wished some dietary help. I really feel it’s possible you’ll make a robust argument that the glycine content material materials is nearly undoubtedly driving the results of collagen supplementation (6), and as a fringe revenue, there’s moreover proof linking glycine to raised sleep (7). Kidney stones don’t seem like a notable drawback throughout the longitudinal analysis on collagen supplementation, nonetheless it’s worth noting that collagen is rich in hydroxyproline, which could theoretically improve the prospect of kidney stones (8). As such, aiming for 3-5g of glycine is probably an acceptable completely different to taking 10-15g of collagen. So, in summary, there’s some proof linking collagen supplementation to modest benefits related to connective tissues and joints, nonetheless it’s pretty doable that just a little bit little little bit of glycine would do the trick. Each method, you don’t want to rely carefully on collagen for the promotion of muscle hypertrophy, and in case you happen to devour a substantial amount of collagen, you’ll want to make sure you’re taking obligatory steps to realize passable and full necessary amino acid consumption.